For patients who undergo mastectomy for the treatment of breast cancer, the restoration of normal breast form through breast reconstruction has been shown to improve their psychological and emotional well being, get rid of external prosthesis, be able to wear many type of clothing and to regain their feminity. This can be achieved using an implant. Using this technique, can produce excellent results in the well selected patient, and compared with autologous tissue reconstruction, implant reconstruction offers a shorter operative procedure with a less down time and no donor site morbidity. It also allows for much easier detection of cancer recurrence.
Reconstruction options for implant-based reconstruction include: single-stage reconstruction with a standard or adjustable implant, or two- staged with tissue expansion followed by placement of a permanent implant, or combined autologous tissue/ implant reconstruction, with or without fat grafting. Procedure selection is based on a range of patient variables, including: availability of local, regional and distant donor tissue, size and shape of the desired breast(s), surgical risk (Hershman et al. (2012) reported that the immediate in -hospital complication rate was significantly higher in patients who underwent autologous reconstruction when compared to those who had prosthetic reconstruction. Most importantly is patient preference. Individualizing selection of a reconstructive technique for each patient will be the predominant factor in achieving a reconstructive success.
Dr Yap believes the most aesthetically pleasing result regarding both shape, consistency, and similarity, are the round, smooth surfaced Motiva silicone gel prosthesis.
Other options are anatomical shape silicone gel, and Normal Saline filled prosthesis. Anatomical shape are less favoured as they have a textured surface to assist preventing rotation. Textured breast implants are associated with a rare form of breast cancer called Lymphoma, and have therefore been warned by the TGA against using. There is no evidence to suggest that the silicone gel prosthesis offer any health risks. The manufacturing technology has improved dramatically in prosthesis that are approved by the TGA, and there is now very little risk of rupture, leak or capsular disintegration from wear and tear, as there was 15 years ago. Both Mentor and Spiran brands carry the option of buying a lifetime warranty.
Single Stage Breast Prosthetic Reconstruction
After a mastectomy, there is very little tissue remaining between the skin and chest wall muscle (pectoral muscle). Prosthesis are therefore placed under the pectoral muscle, within a muscular pocket. The pectoral muscle does not extend across the whole chest wall, and becomes deficient at the lower and outer aspect when the prosthesis is placed under it.
In a single stage reconstruction, other material needs to be sutured to the bottom of this muscle, to create a sling, to hold the prosthesis in a pocket. This can be either alloderm graft from cadaver, or material from cow or pig intestine, or a synthetic mesh.
Recently these products have been used to create a full pocket that sits around the prosthesis and is sutured in front and to the pectoral muscle, holding the prosthesis in front of the muscle to avoid having to lift the muscle from its original position and thus allows for faster healing time.
Breast Prosthetic Reconstruction Procedure
The procedure is performed under general anaesthetic immediately after the skin sparing mastectomy. It adds another 30-60 mins per breast, to the operating time.
There is usually one to two drains used in the procedure. Intravenous antibiotics preferable whilst drains are in.
Time in hospital: 5-7 Days due to drainage (3-5 Days if discharge home with drains in situ).
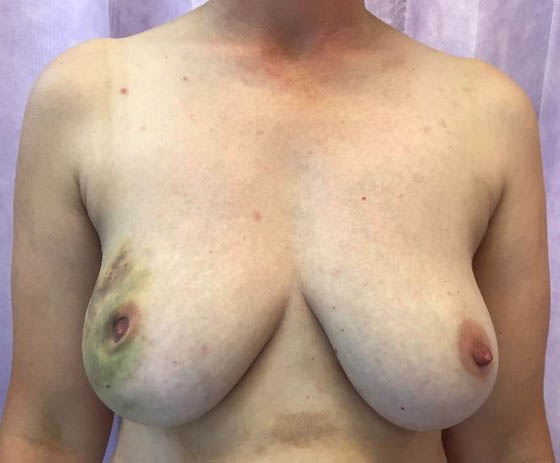
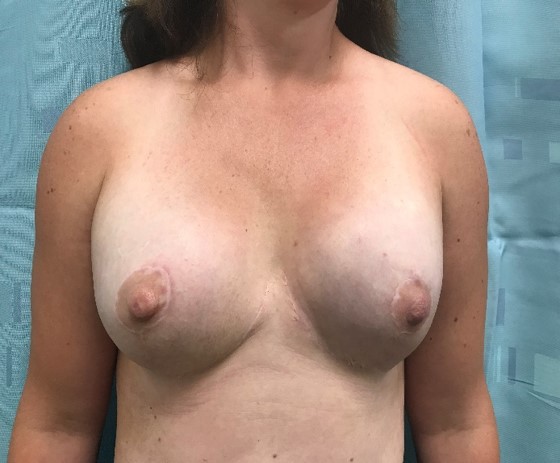
Before and After Breast Prosthetic Reconstruction
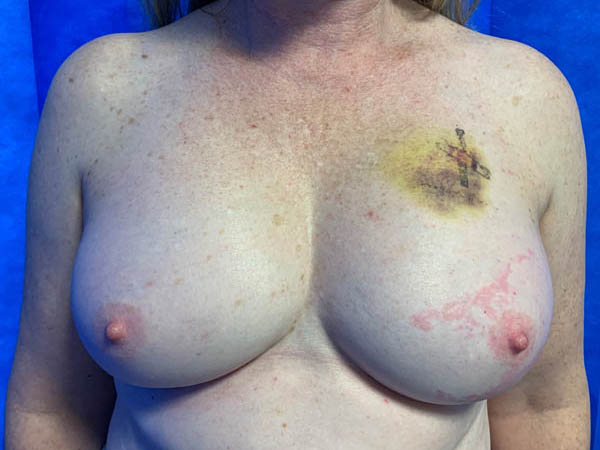
Pre operative left breast cancer following biopsy
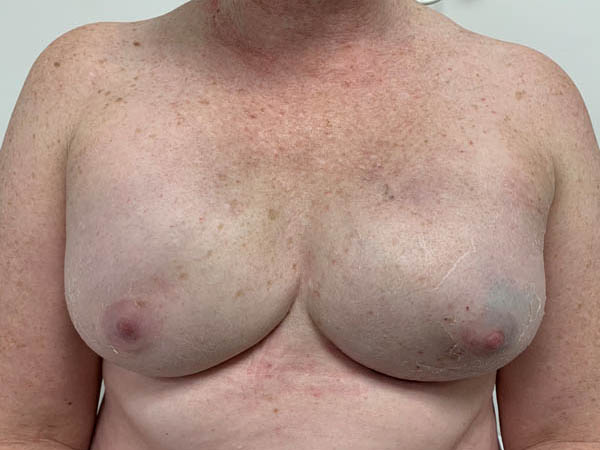
Post operative bilateral skin and nipple-areolar sparing IMMEDIATE prosthetic-based reconstruction
Potential Complications
- Skin loss
- Infection
- Haematoma
- Capsular Contraction
- Seroma formation
- Implant extrusion
- Rippling
Post Operative Care:
- No driving 2-3 weeks
- No heavy lifting for 6 weeks
Breast Prosthetic Reconstruction (Two Stage)
This procedure can be performed as immediate or delayed reconstruction.
It enables the prosthesis to sit under full muscle coverage. This is a better technique in that it allows for better preservation of the nipple-areolar complex, and also affords protection of the implant against involvement with potential complication of post-operative infection. Importantly, it allows the patient more input into the eventual size of their reconstructed breast. This empowerment is very important for women undergoing treatment for breast cancer.
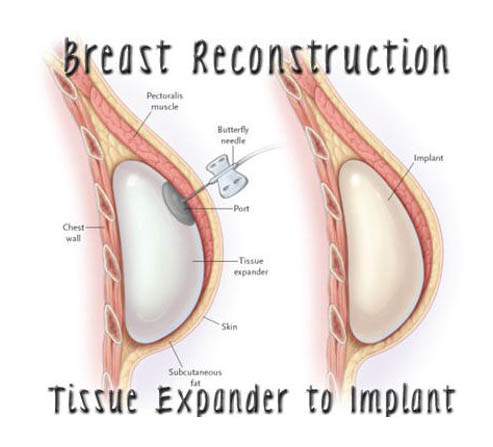
First Stage Prosthetic Procedure
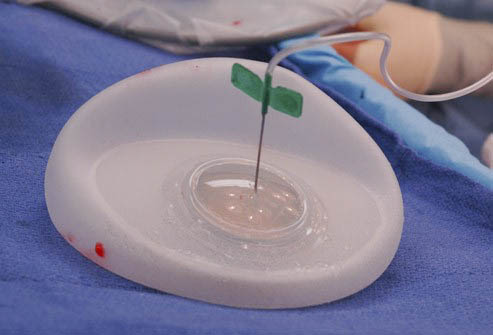
Submuscular insertion of an EXPANDER. This is an empty silicone bag with a valve.
This is placed under the pectoral muscle and sutured into this submuscular pocket. Once the pocket has healed (5-6 weeks), expansion of this bag occurs, usually in the rooms. A magnet is used to locate the valve, and Normal Saline is inserted via a needle into the valve.
The amount of solution injected depends on the patient’s tolerance to the muscle pocket becoming tighter and firmer. This is done serially, on a number of occasions, until the desired volume is achieved. Two drains are inserted per breast.
First Stage Insertion Expander
- Under general anaesthetic , approximately 30-60 m
- Time in hospital depends on drainage (average 4-5 days) Patients can go home with drains in situ in some circumstances
Second Stage Prosthetic Procedure
The expander is removed after the volume inserted is calculated, to allow for the selected volume of definitive silicone gel prosthesis to be inserted into the submuscular pocket.
Second Stage Expander Exchanged to Implant
Procedure:
Under general anaesthetic, 30 -120 mins. Insertion of one drain.
Time in hospital average is 1-3 days.
Post Operative Care:
• No driving for 2 weeks
• No heavy lifting for 6 weeks
Potential Complications
- Deflation of expander
- Infill valve problems of expander
- Infection
- Skin loss
The Complication Rate are increased with:
- Smoking – 2.2X
- Age >65 – 2.5 X
- Obesity and hypertension – 2X
- Radiotherapy – 5X
Total loss of the implant (failure) has an increased risk with:
- Obesity – 7X
- Smoking – 5X
- Hypertension – 4X
- Radiotherapy – 5X